Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
藤原 比呂*; 戸田 裕之*; 海老原 健一; 小林 正和*; 眞山 剛*; 平山 恭介*; 清水 一行*; 竹内 晃久*; 上椙 真之*
International Journal of Plasticity, 174, p.103897_1 - 103897_22, 2024/03
被引用回数:0高強度化したアルミ合金において水素脆化は、理解し解決すべき問題である。アルミ合金において、水素が析出物界面に蓄積し脆化の原因となっていると考えられている。しかし、き裂付近の水素分布と応力場の局所的な相互作用について、空間的な複雑さを考慮した定量的な知見は明らかでない。本研究では、結晶塑性有限要素法と水素拡散解析を組み合わせたマルチモーダル3次元画像ベースシミュレーションを用い、実際のき裂近傍の応力分布と、それが水素分布に及ぼす影響およびき裂発生確率に及ぼす影響を捉えることを試みた。その結果、粒界き裂は、その先端近傍の水素蓄積により、MgZn 析出物の半整合界面の凝集エネルギーが低下した領域で擬へき開き裂に遷移することが分かった。この結果は、本シミュレーション手法がナノスケールの剥離とマクロスケールの脆性破壊の橋渡しに成功したことを示すものと考える。
析出物の半整合界面の凝集エネルギーが低下した領域で擬へき開き裂に遷移することが分かった。この結果は、本シミュレーション手法がナノスケールの剥離とマクロスケールの脆性破壊の橋渡しに成功したことを示すものと考える。
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; 徐 平光; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.04(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The quasi-static superelastic responses and hierarchical martensite transformation from body-centered cubic (BCC) to face-centered cubic (FCC) under dynamic impact in Fe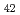 Mn
Mn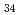 Al
Al Ni
Ni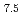 Ti
Ti alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC
alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC  FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
 Cl dissociation, CH
Cl dissociation, CH abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH
abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)
Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)牧野 隆正*; 津田 泰孝; 吉越 章隆; Di o, W. A.*; 岡田 美智雄*
o, W. A.*; 岡田 美智雄*
Applied Surface Science, 642, p.158568_1 - 158568_6, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)To study the elementary steps in the Rochow-Muller process, we bombarded Cu(111) and Cu(410) with 0.7-1.9 eV supersonic molecular beams (SSMB) of CH Cl. We then identified the corresponding adsorbed species using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) in conjunction with synchrotron radiation (SR). We found Cl as the dominant adsorbed species (much higher than that of adsorbed carbonaceous species) coming from the dissociative scattering of CH
Cl. We then identified the corresponding adsorbed species using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) in conjunction with synchrotron radiation (SR). We found Cl as the dominant adsorbed species (much higher than that of adsorbed carbonaceous species) coming from the dissociative scattering of CH Cl. We also found that the threshold kinetic energy of the reaction depends on the crystal surface orientation.
Cl. We also found that the threshold kinetic energy of the reaction depends on the crystal surface orientation.
池田 一貴*; 佐次田 頌*; 大友 季哉*; 大下 英敏*; 本田 孝志*; 羽合 孝文*; 齋藤 開*; 伊藤 晋一*; 横尾 哲也*; 榊 浩司*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Low-vanadium-concentration alloys have low durability, and their hydrogen absorption and desorption amounts decrease by 20% after 100 cycles. In this study, we conducted reverse Monte Carlo modeling on X-ray diffraction patterns and neutron pair distribution functions of the hydrogen-absorbed and desorbed samples of a V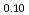 Ti
Ti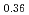 Cr
Cr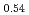 alloy to analyze the variations in the local structure. The local structure surrounding the hydrogen atom in the hydrogen-absorbed phase exhibited minimal changes. In contrast, hydrogen occupied both tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the hydrogen-desorbed phase almost equally during the early cycles; however, the amount of hydrogen occupying the tetrahedral sites increased with the number of cycles.
alloy to analyze the variations in the local structure. The local structure surrounding the hydrogen atom in the hydrogen-absorbed phase exhibited minimal changes. In contrast, hydrogen occupied both tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the hydrogen-desorbed phase almost equally during the early cycles; however, the amount of hydrogen occupying the tetrahedral sites increased with the number of cycles.
Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; 藤原 比呂*; 清水 一行*; 平山 恭介*; 海老原 健一; 竹内 晃久*; 上椙 真之*; 戸田 裕之*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金の外部および内部水素(H)の組合せによって誘起される応力腐食割れ(SCC)の挙動をその場3次元評価技術を使い系統的に調べた。Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金のSCCは水素濃度が臨界値を超える潜在的なクラック発生領域で発生・進展し、Hがナノスケール -MgZn
-MgZn 析出物界面での原子結合を弱め巨視的な割れを引き起こしていることが分かった。さらに、水環境からき裂へ浸透した外部Hが、き裂先端近傍に勾配を持つH影響ゾーンを作ることでSCCにおいて重要な役割を果たすことや、あらかじめ存在する内部Hが、塑性変形に伴いき裂先端に向かうことでSCCにおけるき裂の発生と進展の両方に関与することも分かった。
析出物界面での原子結合を弱め巨視的な割れを引き起こしていることが分かった。さらに、水環境からき裂へ浸透した外部Hが、き裂先端近傍に勾配を持つH影響ゾーンを作ることでSCCにおいて重要な役割を果たすことや、あらかじめ存在する内部Hが、塑性変形に伴いき裂先端に向かうことでSCCにおけるき裂の発生と進展の両方に関与することも分かった。
Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 徐 平光; 行武 栄太郎*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 23 Pages, 2024/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnesium alloy AZ31, which has undergone high-pressure torsion processing, was subjected to in situ annealing micro-beam synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction and compared to the as-received rolled sheet material that was investigated through in situ neutron diffraction. While the latter only exhibits thermal expansion and minor recovery, the nanostructured specimen displays a complex evolution, including recovery, strong recrystallization, phase transformations, and various regimes of grain growth. Nanometer-scale grain sizes, determined using Williamson-Hall analysis, exhibit seamless growth, aligning with the transition to larger grains, as assessed through the occupancy of single grain reflections on the diffraction rings. The study uncovers strain anomalies resulting from thermal expansion, segregation of Al atoms, and the kinetics of vacancy creation and annihilation. Notably, a substantial number of excess vacancies were generated through high-pressure torsion, and maintained for driving the recrystallization and forming highly activated volumes for diffusion and phase precipitation during heating. The unsystematic scatter observed in the Williamson-Hall plot indicates high dislocation densities following severe plastic deformation, which significantly decreases during recrystallization. Subsequently, dislocations reappear during grain growth, likely in response to torque gradients in larger grains. It is worth noting that the characteristics of unsystematic scatter differ for dislocations created at high and low temperatures, underscoring the strong temperature dependence of slip system activation.
比嘉 良太*; 藤原 比呂*; 戸田 裕之*; 小林 正和*; 海老原 健一; 竹内 晃久*
軽金属, 73(11), p.530 - 536, 2023/11
Al-Zn-Mg合金において、その強度向上には水素脆化の抑制が必要である。本研究では、X線CTから得られた3次元多結晶微細構造データに基づくモデルによる結晶塑性有限要素法及び水素拡散解析を用いて、実際の破断領域における応力、ひずみ及び水素濃度の分布を調べた。さらに、引張試験のX線CTによるその場観察とシミュレーションを組み合わせて、応力、ひずみ、水素濃度の分布と実際のき裂発生挙動を比較した。その結果、結晶塑性に起因する粒界に垂直な応力負荷が主に粒界き裂発生を支配することが明らかになった。また、結晶塑性に起因する内部水素の蓄積は、き裂発生にほとんど影響しないことがわかった。
山口 正剛; 海老原 健一; 都留 智仁; 板倉 充洋
Materials Transactions, 64(11), p.2553 - 2559, 2023/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)アルミニウム合金中のMgZn 析出物とMg
析出物とMg Si晶出物の非整合界面における水素トラップエネルギーを第一原理計算から計算することを試みた。非整合界面を含む単位胞は周期境界条件を満たさず、結晶ブロックが不連続になるため、不連続領域(真空領域)から離れた領域で水素トラップエネルギーを計算した。その結果、この原子論的配置を仮定した非整合界面では、水素原子のトラップエネルギーがかなり大きいことがわかった。また、アルミニウム母相中のMg
Si晶出物の非整合界面における水素トラップエネルギーを第一原理計算から計算することを試みた。非整合界面を含む単位胞は周期境界条件を満たさず、結晶ブロックが不連続になるため、不連続領域(真空領域)から離れた領域で水素トラップエネルギーを計算した。その結果、この原子論的配置を仮定した非整合界面では、水素原子のトラップエネルギーがかなり大きいことがわかった。また、アルミニウム母相中のMg Siの非整合界面における水素トラップによる凝集エネルギーの減少についても予備的計算を行った。
Siの非整合界面における水素トラップによる凝集エネルギーの減少についても予備的計算を行った。
 MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発
MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発伊東 達矢; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
物性研だより, 63(3), p.8 - 10, 2023/10
メタ磁性形状記憶合金は磁場により駆動することが出来る形状記憶合金であり、センサーやアクチュエーター等での応用が期待されている。しかし、これまでに開発されてきた合金系ではマルテンサイト変態に伴うエネルギーロスが大きいという問題点があった。近年、我々の研究グループではPd MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
池田 陽一*; 梅本 好日古*; 松村 大樹; 辻 卓也; 橋本 勇輝*; 北澤 崇文*; 藤田 全基*
Materials Transactions, 64(9), p.2254 - 2260, 2023/09
被引用回数:0Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and neutron diffraction experiments were carried out to clarify the typical features of the local structure of a family of medium-entropy alloys (CrCoNi, MnCoNi, and FeCoNi). A simple random cluster model was constructed for analyzing EXAFS spectra, and static and dynamic components of the mean-square relative displacement (MSRD) were separately extracted. In our analysis, the static MSRD of the MnCoNi sample was slightly larger than those of the CrCoNi and FeCoNi samples, whereas the dynamic MSRDs of these samples were almost identical. Based on the complementary neutron diffraction data, we argued that the origin of the large static displacement in the MnCoNi alloy can be associated with a short-range structural transformation through long-term structural relaxation.
Liss, K.-D.*; 徐 平光; 城 鮎美*; Zhang, S. Y.*; 行武 栄太郎*; 菖蒲 敬久; 秋田 貢一*
Advanced Engineering Materials, 9 Pages, 2023/00
In polycrystals, grains with certain orientations grow at high temperatures at the expense of grains with other unfavorable orientations. Grain growth involves a variety of situations and mechanisms that make experimental study, modeling, and understanding extremely complex. Normal grain growth occurs in a self-similar manner, with curved grain boundaries serving as the driving force and a parabolic growth law that scales up the grain size by the square root of time. More complex growth forms include boundary pinning of precipitates and other boundaries, topological transitions that alter driving forces, grain coalescence and anomalous grain growth, but these are considered "erratic" and their initiation is an open question in modern research, without a simple experimental approach on how they should be studied. Here, we show that grain rotation upon coalescence is spontaneously activated between one grain and a favorable neighbor, through the necessary diffusive mass transport at further boundaries of the same grain leading to their activation and a competitive "erratic" reorientation in a zigzag way, while other grains in the matrix remain stable. After two grains have eventually coalesced, their surrounding boundaries are still activated leading to further rotation and growth, filling the missing puzzle stone in thermodynamic theory between normal and abnormal growth, the latter stating that abnormal growth only takes place when the size of the growing grain is already large. Prerequisites and postulates of abnormal grain growth are based on advantageous texture, grain boundary mobility, enhanced diffusion kinetics and coalescence, which can be well explained by our observations. Moreover, our observations have been enabled through a novel experimental approach using the white-beam X-ray Laue diffraction method in bulk transmission mode on a polycrystalline.
Liu, X. J.*; 徐 平光; 城 鮎美*; Zhang, S. Y.*; 菖蒲 敬久; 行武 栄太郎*; 秋田 貢一*; Zolotoyabko, E.*; Liss, K.-D.*
Journal of Materials Science, 57(46), p.21446 - 21459, 2022/12
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:41.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In situ time/temperature-resolved synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction is applied to study heat-mediated structural changes and phase transformations in rolled sheets of AZ91 and AZ31 magnesium alloys. Azimuthal diffraction intensities along the Debye-Scherrer rings (AT-plots) are used to obtain information on grain recovery and recrystallization temperatures as well as temperature-assisted grain rotations. The azimuthally integrated diffraction intensities, plotted as functions of the scattering vector (QT-plots), provide vital data on the temperature-dependent lattice parameters of the Mg/Al matrix and intermetallic precipitates, as well as on the evolution of the precipitates' volume fraction. It was found that in AZ31, the main precipitates are of the AlMn type, which is rather stable in the investigated temperature range (up to 773 K). In contrast, in AZ91, the major intermetallic precipitates, Al Mg
Mg , undergo complete dissolution above 600 K. It is caused by the enhanced diffusion of Al into the Mg/Al matrix, which according to the Al-Mg phase diagram, can adopt more Al at elevated temperatures. This diffusion is revealed by the proportional diminishing of the matrix lattice parameter (chemical strain), allowing us to quantify the Al content in the matrix. Fast temperature-dependent manipulation with intermetallic content in the Mg/Al alloy can, in principle, be used for controlling its mechanical properties.
, undergo complete dissolution above 600 K. It is caused by the enhanced diffusion of Al into the Mg/Al matrix, which according to the Al-Mg phase diagram, can adopt more Al at elevated temperatures. This diffusion is revealed by the proportional diminishing of the matrix lattice parameter (chemical strain), allowing us to quantify the Al content in the matrix. Fast temperature-dependent manipulation with intermetallic content in the Mg/Al alloy can, in principle, be used for controlling its mechanical properties.
Xu, X.*; 大平 拓実*; Xu, S.*; 平田 研二*; 大森 俊洋*; 植木 洸輔*; 上田 恭介*; 成島 尚之*; 長迫 実*; 貝沼 亮介*; et al.
Advanced Materials & Processes, 180(7), p.35 - 37, 2022/10
Metallic biomaterials are widely used to replace or support failing hard tissues due to excellent mechanical properties and high wear resistance, with demand increasing as the global population continues to age. It is widely accepted that successful metallic biomaterials should have good biocompatibility, high corrosion resistance, and strong wear resistance. In addition, a low Young's modulus similar to human bone is now recognized as another important factor, in order to avoid bone atrophy due to the stress shielding effect. While the Young's modulus of stainless steels and conventional fcc CoCr alloys is as high as 190-240 GPa, for  -type Ti-base alloys it is generally in the range of 50-80 GPa. Young's modulus values are as low as 35 GPa for Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr, close to that of human bone at approximately 10-30 GPa. However, Ti-base alloys come with the compromise of low wear resistance. In fact, alloys that feature a low Young's modulus along with high wear resistance have been difficult to realize. This article explores the recently developed bcc CoCr-base alloy Co-Cr-Al-Si as a potential solution to these issues, i.e., the difficulty in combining a low Young's modulus with high wear resistance, and the challenge of realizing large superelastic strains.
-type Ti-base alloys it is generally in the range of 50-80 GPa. Young's modulus values are as low as 35 GPa for Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr, close to that of human bone at approximately 10-30 GPa. However, Ti-base alloys come with the compromise of low wear resistance. In fact, alloys that feature a low Young's modulus along with high wear resistance have been difficult to realize. This article explores the recently developed bcc CoCr-base alloy Co-Cr-Al-Si as a potential solution to these issues, i.e., the difficulty in combining a low Young's modulus with high wear resistance, and the challenge of realizing large superelastic strains.
城 鮎美*; 菖蒲 敬久; 萩原 幸司*; 渡邉 真史*
SPring-8/SACLA利用研究成果集(インターネット), 10(5), p.438 - 446, 2022/10
長周期積層型(LPSO)マグネシウム合金は、濃度と構造の変調が同期しており、軽量かつ高強度・高耐熱性という性質を併せ持った新規材料である。LPSO相の局所的な格子ひずみと構造変調の関係を調べるために、単相18R LPSO Mg-Zn-Y合金の圧縮下での 放射光X線回折測定を実施した。圧縮応力の増加に伴い、格子ひずみの増加が確認されるとともに、0 0 L回折面からの回折強度の大小が入れ替わる現象が発生した。解析の結果、回折強度の変化はイットリウム原子の特徴的な変位によるものであり、弾性変形から塑性変形への移行に大きな影響を与える可能性を明らかにした。
放射光X線回折測定を実施した。圧縮応力の増加に伴い、格子ひずみの増加が確認されるとともに、0 0 L回折面からの回折強度の大小が入れ替わる現象が発生した。解析の結果、回折強度の変化はイットリウム原子の特徴的な変位によるものであり、弾性変形から塑性変形への移行に大きな影響を与える可能性を明らかにした。
榊 浩司*; Kim, H.*; Majzoub, E. H.*; 町田 晃彦*; 綿貫 徹*; 池田 一貴*; 大友 季哉*; 水野 正隆*; 松村 大樹; 中村 優美子*
Acta Materialia, 234, p.118055_1 - 118055_10, 2022/08
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:83.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Local structure in the di-hydride phases of V-Ti-Cr solid solution alloys were investigated using synchrotron X-ray and neutron total scattering experiments. Both Rietveld refinement and pair distribution function (PDF) refinement of the X-ray scattering data indicated that the crystal structure of the metal lattice was a face centered cubic (FCC) structure and no difference between their local structure and average structure was observed. However, the CaF structure model did not reproduce the first peak corresponding to the metal-hydrogen correlation in neutron PDF patterns. When special quasi-random structure (SQS) models are applied for the refinements, the whole neutron PDF patterns were reproduced. Distribution of interatomic distances between hydrogen and metal atoms in the relaxed SQS models showed that interatomic distance of hydrogen with Cr was shorter than that with V and that with Ti was longer than that with V, independently of the chemical compositions.
structure model did not reproduce the first peak corresponding to the metal-hydrogen correlation in neutron PDF patterns. When special quasi-random structure (SQS) models are applied for the refinements, the whole neutron PDF patterns were reproduced. Distribution of interatomic distances between hydrogen and metal atoms in the relaxed SQS models showed that interatomic distance of hydrogen with Cr was shorter than that with V and that with Ti was longer than that with V, independently of the chemical compositions.
津田 泰孝; Gueriba, J. S.*; 植田 寛和*; Di o, W. A.*; 倉橋 光紀*; 岡田 美智雄*
o, W. A.*; 倉橋 光紀*; 岡田 美智雄*
JACS Au (Internet), 2(8), p.1839 - 1847, 2022/08
The orientation and motion of reactants play important roles in reactions. The small rotational excitations involved render the reactants susceptible to dynamical steering, making direct comparison between experiment and theory rather challenging. Using space quantized molecular beams, we directly probe the (polar and azimuthal) orientation dependence of O chemisorption on Cu
chemisorption on Cu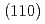 and Cu
and Cu Au
Au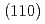 . We observe polar and azimuthal anisotropies on both surfaces. Chemisorption proceeds rather favorably with the O-O bond axis oriented parallel (
. We observe polar and azimuthal anisotropies on both surfaces. Chemisorption proceeds rather favorably with the O-O bond axis oriented parallel (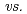 perpendicular) to the surface, and also rather favorably with the O-O bond axis oriented along
perpendicular) to the surface, and also rather favorably with the O-O bond axis oriented along ![$$[001]$$](/search/images/ERNTAMBRLUSA.gif) (
(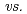 along
along ![$$[bar{1}10]$$](/search/images/ERNVYYTBOJ3TC5JRGBOSI.gif) ). The presence of Au hinders the surface from further oxidation, introducing a higher activation barrier to chemisorption, and rendering an almost negligible azimuthal anisotropy. The presence of Au also prevents cartwheel-like rotating O
). The presence of Au hinders the surface from further oxidation, introducing a higher activation barrier to chemisorption, and rendering an almost negligible azimuthal anisotropy. The presence of Au also prevents cartwheel-like rotating O from further reactions.
from further reactions.
大平 拓実*; Xu, S.*; 平田 研二*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 植木 洸輔*; 上田 恭介*; 成島 尚之*; 長迫 実*; Harjo, S.; et al.
Advanced Materials, 34(27), p.2202305_1 - 2202305_11, 2022/07
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:87.73(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The demand for biomaterials has been increasing along with the increase in the population of elderly people worldwide. The mechanical properties and high wear resistance of metallic biomaterials makes them well-suited for use as substitutes or as support for damaged hard tissues. However, unless these biomaterials also have a low Young's modulus similar to that of human bones, bone atrophy inevitably occurs. Because a low Young's modulus is typically associated with poor wear resistance, it is difficult to realize a low Young's modulus and high wear resistance simultaneously. Also, the superelastic property of shape memory alloys makes them suitable for biomedical applications, like vascular stents and guide wires. However, due to the low recoverable strain of conventional biocompatible shape memory alloys, the demand for a new alloy system is high. The novel body-center-cubic cobalt-chromium-based alloys in this paper provide a solution to both of these problems. We believe our novel alloys are promising candidates for biomedical applications.
垣内 一雄; 宇田川 豊; 山内 紹裕*
JAEA-Research 2022-001, 21 Pages, 2022/06
冷却材喪失事故(LOCA)時想定される被覆管脆化の主たる要因は、高温酸化に伴う金属層中酸素濃度の増大とこれに起因する微細組織の変化である。被覆管が破裂した場合には、燃料棒内に侵入した水蒸気によって生じる被覆管内面の酸化及びこれに伴う燃料棒内水素分圧の上昇の結果、破裂開口部からやや離れた軸方向位置で局所的な水素吸収が起こり(二次水素化)、二次水素化部では水素脆化による延性低下も重畳する。これら微細組織の変化がLOCA条件下における燃料棒の機械特性に及ぼす影響をより詳細かつ定量的に把握するため、LOCA模擬試験後試料の破裂開口部及び二次水素化部の延性評価にナノインデンテーション法を適用した。硬さやヤング率に加えて、押込み荷重-変位曲線から算出される塑性仕事割合を評価したところ、二次水素化部の金属層(prior- 相)における塑性仕事割合は、被覆管外周のZrO
相)における塑性仕事割合は、被覆管外周のZrO 層と
層と -Zr(O)層に近い水準であり、破裂開口部に比べて酸素濃度が低いにもかかわらず、水素の影響により有意に延性が低下していることが示唆された。
-Zr(O)層に近い水準であり、破裂開口部に比べて酸素濃度が低いにもかかわらず、水素の影響により有意に延性が低下していることが示唆された。
 during high temperature deformation
during high temperature deformationJaladurgam, N. R.*; Lozinko, A.*; Guo, S.*; Harjo, S.; Colliander, M. H.*
Materialia, 22, p.101392_1 - 101392_4, 2022/05
The load redistribution between and within phases in eutectic high entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNi was measured using in-situ neutron diffraction during tensile deformation at 973 K. The load partitioning between phases is reversed compared to lower temperatures, with L1
was measured using in-situ neutron diffraction during tensile deformation at 973 K. The load partitioning between phases is reversed compared to lower temperatures, with L1 becoming the stronger phase. The evolution of the orientation-specific stresses and strains in the L1
becoming the stronger phase. The evolution of the orientation-specific stresses and strains in the L1 phase suggests that cube slip dominates the response. The low strength, internal load transfer and ideally plastic response of the B2 phase indicate a change in deformation mechanism compared to lower temperatures.
phase suggests that cube slip dominates the response. The low strength, internal load transfer and ideally plastic response of the B2 phase indicate a change in deformation mechanism compared to lower temperatures.
 TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloy
TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloyChen, J.*; 吉田 健太*; 鈴土 知明; 嶋田 雄介*; 井上 耕治*; 今野 豊彦*; 永井 康介*
Materials Transactions, 63(4), p.468 - 474, 2022/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:17.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)高分解能透過型電子顕微鏡(HRTEM)を用いてその場電子照射により、アルミニウム-銅(Al-Cu)合金のフランクループの発達を0.12nmの原子スケールの空間分解能で視覚化した。FCC-Al格子の[110]方向に沿ったその場HRTEM観察では、固有の積層欠陥の境界となるフランク部分転位は、純Al参照サンプルの場合とは異なり、 112
112 方向に沿って非対称の上昇を示した。この時の弾き出し損傷率は0.055-0.120dpa/sであった。分子動力学シミュレーションによって、この部分転位の非対称上昇はギニア-プレストンゾーン(GPゾーン)でのCu-Cu結合によるピン止め効果として説明された。
方向に沿って非対称の上昇を示した。この時の弾き出し損傷率は0.055-0.120dpa/sであった。分子動力学シミュレーションによって、この部分転位の非対称上昇はギニア-プレストンゾーン(GPゾーン)でのCu-Cu結合によるピン止め効果として説明された。